| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
- algorithm
- Python
- 프로그래머스
- 프로그래밍
- androidstudio
- 리액트네이티브
- 알고리즘
- 동적계획법
- 백준
- 자바
- Android
- 코딩
- 씨쁠쁠
- 개발자
- 비전공자를위한이해할수있는IT지식
- IT도서
- 파이썬
- 안드로이드
- kotlin
- C++
- programming
- 코딩테스트
- PS
- java
- 웹
- 자료구조
- DP
- 앱개발
- Coding
- 안드로이드스튜디오
- Today
- Total
한 발짜국
알고리즘 #12 (DP, 백준 2579번) [C++] 본문
DP 두번째!
DP 초보자로서
https://zzonglove.tistory.com/13
동적계획법 (Dynamic Programming) 는 어떻게 풀까?
이 포스팅은 Nitish Kumar 의 기사를 참고하여 만들었습니다. [출처] 동적계획법 (Dynamic Programming), DP 는 다항(Polynomial)한 시간안에 특정 문제를 풀기위한 기술입니다. DP 를 이용한 솔루션은 지수형태
zzonglove.tistory.com
이 게시글의 동적계획법 푸는 순서을 한 번 따라해보려했다.
[백준 2579번]
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2579
2579번: 계단 오르기
계단 오르기 게임은 계단 아래 시작점부터 계단 꼭대기에 위치한 도착점까지 가는 게임이다. <그림 1>과 같이 각각의 계단에는 일정한 점수가 쓰여 있는데 계단을 밟으면 그 계단에 쓰여 있는 점
www.acmicpc.net
계단 1개 → {1}
계단 2개 → {1, 2}, {2}
계단 3개 → {1, 3}, {2, 3}
계단 4개 → {1, 2, 4}, {1, 3, 4}, {2, 4}
계단 5개 → {1, 2, 4, 5}, {1, 3, 5}, {2, 3, 5}, {2, 4, 5}
...
규칙은 n개의 계단일 때 경우의 수가
n-2개의 계단의 경우의 수 + n-3개의 계단의 경우의 수 라는 것이었다.
이를 이용해서 n개의 계단일 때 계단의 수를 구하고 그 모든 경우의 수를 총점수를 계산한 후 sort해 최댓값을 구하는 방식으로 코드를 적어봤는데
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void readScore(int& T,vector<int>& scores) {
int score;
cin >> T;
for (int i = 0; i < T; i++) {
cin >> score;
scores.push_back(score);
}
}
vector<vector<int>> nOrders(int n) {
vector<vector<int>> orders;
if (n == 0)
orders = { { 1 } };
else if (n == 1)
orders = { { 1, 2 }, { 2 } };
else if (n == 2)
orders = { { 1, 3 }, { 2, 3 } };
else {
vector<vector<int>> n2 = nOrders(n - 2);
vector<vector<int>> n3 = nOrders(n - 3);
for (int i = 0; i < n2.size(); i++) {
n2[i].push_back(n+1);
orders.push_back(n2[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n3.size(); i++) {
n3[i].push_back(n);
n3[i].push_back(n+1);
orders.push_back(n3[i]);
}
}
return orders;
}
int maxScore(vector<int> scores, vector<vector<int>> orders) {
int totalScore = 0;
vector<int> totalScores;
for (int i = 0; i < orders.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < orders[i].size(); j++) {
totalScore += scores[orders[i][j]];
}
totalScores.push_back(totalScore);
totalScore = 0;
}
sort(totalScores.begin(), totalScores.end());
return totalScores[totalScores.size()-1];
}
int main() {
int T, max;
vector<vector<int>> orders;
vector<int> scores = { 0 };
readScore(T, scores);
orders = nOrders(T - 1);
max = maxScore(scores, orders);
cout << max;
}참.. 길다...
비주얼 스튜디오에서 몇가지 수로 돌려봤을 때 답이 정상적으로 출력됐다. 하지만...
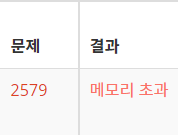
ㅎㅎ... 역시 초보자에게는 호락호락하지 않다.
모를 땐 검색!
항상 느끼지만 정말 잘하시는 분, 똑똑한 분들이 너무 많다.....
https://yabmoons.tistory.com/20
[ 백준 2579 ] 계단오르기 (C++)
백준의 계단오르기(2579) 문제이다. ( 문제 바로가기 ) ( 문제를 다시 푸는 과정에서 보다 상세한 설명을 다시 포스팅 해놓았습니다. 이 글을 읽으셔도 무관하지만, 보다 구체적인 설명을 원하시는
yabmoons.tistory.com
이 분의 코드를 따라하면서 공부했다.
하면서 내 코드가 얼마나 불필요하게 나뉘었는지 정말 많이 느꼈다ㅎ
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#define MAX 301
using namespace std;
int T;
int maxScores[MAX];
int scores[MAX];
int Max(int A, int B) { if (A > B) return A; return B; }
void readScore() {
cin >> T;
for (int i = 1; i <= T; i++) {
cin >> scores[i];
}
}
void maxSum() {
maxScores[1] = scores[1];
maxScores[2] = scores[1]+scores[2];
maxScores[3] = Max(scores[1] + scores[3], scores[2] + scores[3]);
for (int i = 4; i <= T; i++) {
maxScores[i] = Max((maxScores[i - 2] + scores[i]), (maxScores[i - 3] + scores[i - 1] + scores[i]));
}
cout << maxScores[T];
}
int main() {
readScore();
maxSum();
}길이가 확줄었다^^ㅋㅋㅋㅋ
효율적이고 깔끔한 코드다... 진짜 열심히 배워야지...
'알고리즘&자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 알고리즘 #14 (DP, 백준 11722번, 11053번, 11054번) [C++] (0) | 2021.12.28 |
|---|---|
| 알고리즘 #13 (DP, 백준 1463번, 11726번) [C++] (0) | 2021.12.27 |
| 알고리즘 #11 (DP, 백준 2748번, 9095번) [C++] (0) | 2021.12.23 |
| 알고리즘과 자료구조 강의 (feat. 어서와! 자료구조와 알고리즘은 처음이지?) (0) | 2021.12.21 |
| 알고리즘 #10 (재귀 알고리즘) [JAVA] (0) | 2021.10.07 |
